Technical articles
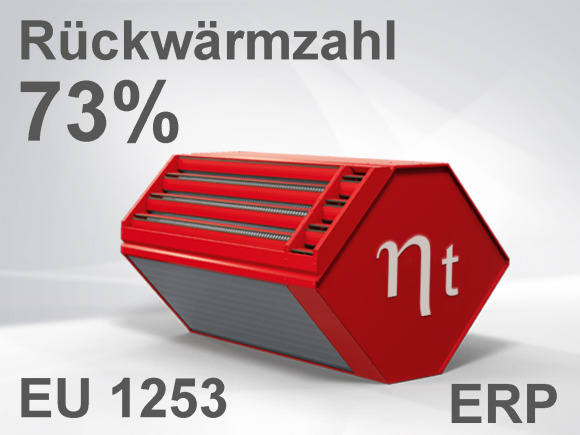
Temperature efficiency values: Definitions and requirements

Condensation in the plate heat exchanger increases efficiency and pressure drop

Regulating output with bypass system
Consider the pressure difference
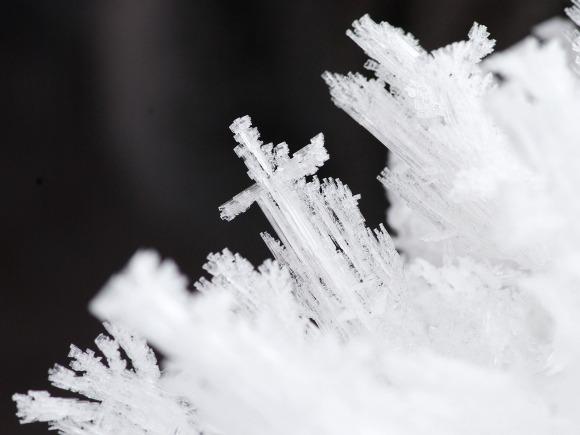

Freezing of condensate in the plate heat exchanger

